Difference Between Array and Pointer
Contents
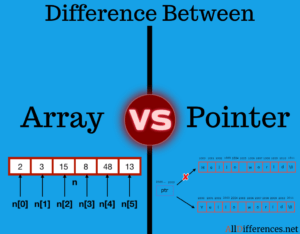
Array and Pointer Difference
The Key Difference Between Array and Pointer is that Array is a collection of variables belongings to the same data type and carries the same size. A Pointer is a single variable that stores the address of another variable.
Comparison Chart
| Array | Pointer |
|---|---|
| Array is a constant pointer. | Pointer variable can be changed. |
| It refers directly to the elements. | It refers address of the variable. |
| Memory allocation is in sequence. | Memory allocation is random. |
| Allocates the memory space which cannot resize or reassigned. | Allocated memory size can be resized. |
| It is a group of elements. | It is not a group of elements. It is a single variable. |
| Array can be initialized at definition. Example int num[] = { 2, 4, 5} |
Pointer can’t be initialized at a definition |
| The assembly code of Array is different than Pointer. | The assembly code of Pointer is different than Array. |
Array
- An array is a fixed-size sequenced collection of elements of the same data type.
- An array is a derived data type.
- The individual elements of an array is referred by their index or subscript value.
- The subscript for an array always begins with 0.
- Syntax:
data_type array_name[size];
- Example:
int marks[5];
- The data_type specifies the type of elements that can be stored in an array, like int, float, or char.
- The size indicates the maximum number of elements that can be stored inside the array.
- In the example, the data type of an array is int and the maximum elements that can be stored in an array are 5.
- Types of an array:
- Single dimensional array
- Two-dimensional array
- Multidimensional array
Advantages of Array
- You can use one array name to store many values with different indexes.
- An array is very useful when you are working with sequences of the same data.
- An array makes the program easier to read, write and debug.
Example
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
int a[10];
int i,j;
for (i = 0;i<10;i++) {
a[i] = i+1;
}
for (j = 0;j<10;j++) {
printf("Element[%d] = %d\n", j, a[j] );
}
return 0;
}
Pointer
- A pointer is a variable that contains an address or location of another variable.
- Pointer is a derived data type in C
- Pointers contain memory addresses as their values, so they can also be used to access and manipulate data stored in memory.
- Syntax: data_type *pt_name;
void main()
{
int a=10,*p;
p = &a; \\ Assign memory address of a to pointer variable p
printf(“%d %d %d”, a, *p, p);
}
- Output: 10 10 5000
- p is integer pointer variable
- & is the address of or referencing operator which returns the memory address of a variable.
- * is an indirection or dereferencing operator which returns the value stored at that memory address.
- & operator is the inverse of * operator ( x = a is same as x = *(&a))
Example
#include<stdio.h>
int main () {
int a = 8;
int *ptr;
ptr = &a;
printf("Value of variable a: %d\n", a);
printf("Address of variable a: %d\n", ptr);
return 0;
}
More Differences
- Difference Between Entry Control Loop and Exit Control Loop
- Difference between Flowchart and Algorithm
